Lambda expressions are a powerful feature in C# that allow you to write concise and flexible code, especially when dealing with collections, delegates, and LINQ (Language-Integrated Query). They are essentially anonymous functions that you can use wherever a delegate type is expected.
In this tutorial, we’ll cover:
- What lambda expressions are.
- The syntax of lambda expressions.
- How they are used in practical scenarios, such as LINQ queries and functional programming.
- A few advanced use cases.
What is a Lambda Expression?
A lambda expression is an anonymous function that can contain expressions and statements. You can use lambda expressions to create delegates or expression tree types.
A simple example of a lambda expression:
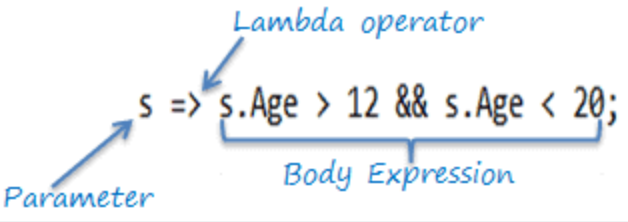
(int x) => x + 1In this case:
(int x)is the input parameter of the lambda expression.=>is the lambda operator.x + 1is the body of the lambda expression, which returnsx + 1.
Lambdas are most often used in scenarios where you need a simple, inline function for tasks such as filtering or transforming data, especially in LINQ queries.
Lambda Expression Syntax
Lambda expressions come in two forms:
- Expression Lambdas: Used for simple expressions. They consist of a single expression and return its result implicitly. Example:
(x, y) => x + y- Statement Lambdas: These are used when you need multiple lines of code. They include a block of code inside curly braces
{}. Example:
(int x, int y) =>
{
int sum = x + y;
return sum;
}In general, the left side contains the input parameters, and the right side defines the logic of the function.
Lambda Expressions in LINQ
One of the most common use cases for lambda expressions is with LINQ (Language-Integrated Query). LINQ enables you to work with collections in a more declarative way. Lambda expressions simplify working with LINQ queries.
Example 1: Using Lambda with Where() in LINQ
The Where() method is used to filter elements in a collection based on a condition. Let’s look at an example where we filter a list of numbers.
List<int> numbers = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
var evenNumbers = numbers.Where(n => n % 2 == 0);
foreach (var num in evenNumbers)
{
Console.WriteLine(num); // Outputs 2, 4, 6, 8
}In this example:
n => n % 2 == 0is the lambda expression, wherenis each element in the list.Where()filters numbers that satisfy the conditionn % 2 == 0.
Example 2: Using Lambda with Select() in LINQ
The Select() method is used to project each element of a collection into a new form.
var squaredNumbers = numbers.Select(n => n * n);
foreach (var num in squaredNumbers)
{
Console.WriteLine(num); // Outputs squares of each number: 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81
}Here, the lambda expression n => n * n multiplies each element in the numbers list by itself.
Lambda Expressions and Delegates
A lambda expression can be assigned to a delegate, which is a type-safe function pointer.
Func<int, int, int> add = (x, y) => x + y;
int result = add(5, 10);
Console.WriteLine(result); // Outputs 15Func<int, int, int>is a delegate that represents a function taking two integers and returning an integer.- The lambda expression
(x, y) => x + ymatches the signature of theFuncdelegate.
Predicate Example with Lambda
A Predicate<T> delegate represents a method that takes a value of type T and returns a boolean. Here’s an example using a predicate:
List<int> numbers = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
Predicate<int> isEven = num => num % 2 == 0;
List<int> evenNumbers = numbers.FindAll(isEven);
foreach (var num in evenNumbers)
{
Console.WriteLine(num); // Outputs 2, 4, 6
}The lambda expression num => num % 2 == 0 acts as a predicate to find all even numbers in the list.
Advanced Use Cases of Lambda Expressions
1. Using Lambda with Events
Lambda expressions can also be used in event handling.
button.Click += (sender, e) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Button was clicked!");
};This is a cleaner way of subscribing to events compared to defining a separate method.
2. Expression Trees
Lambda expressions can be compiled into expression trees, which are representations of code in a tree-like structure. This is useful in scenarios where the code needs to be modified or executed dynamically.
Expression<Func<int, bool>> expr = num => num > 5;
Console.WriteLine(expr.Body); // Outputs num > 5Expression trees are especially powerful in LINQ-to-SQL or Entity Framework, where queries can be dynamically built and optimized before being executed against a database.
Conclusion
Lambda expressions in C# are a concise way to define inline functions. They are extremely useful in scenarios like LINQ queries, event handling, and working with delegates. They help you write more readable, compact, and functional-style code, which is especially useful when working with collections.
Key Resources for Learning More
With lambda expressions, you’ll be able to write more concise and readable code while embracing a more functional style of programming in C#.


Leave a Reply