In C programming, arrays are a powerful data structure used to store a collection of elements of the same type. Arrays in C are helpful when you need to work with a fixed number of data items, such as a list of integers, characters, or floating-point numbers.
In this post, we’ll cover the basics of arrays in C, including how to declare and initialize them, access elements, and common use cases, along with examples.
What is an Array?
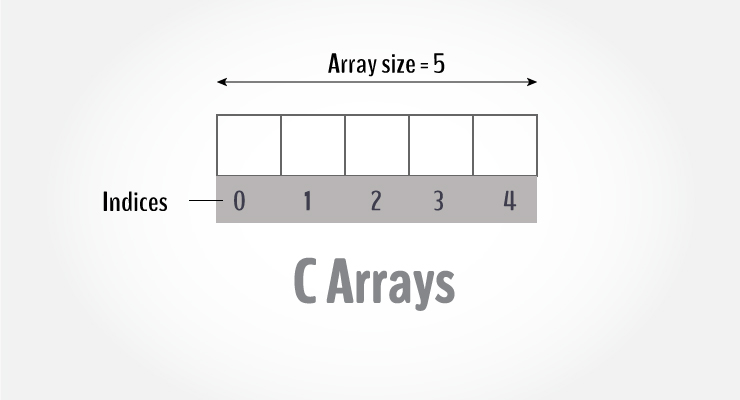
An array is a contiguous block of memory that holds multiple values of the same type. All elements of an array are stored at contiguous memory locations, and each can be accessed using an index. The index starts at 0, so the first element is at position 0, the second at position 1, and so on.
Syntax:
data_type array_name[array_size];data_type: Type of elements (e.g.,int,float,char).array_name: Name of the array.array_size: Number of elements the array will hold.
Declaring and Initializing Arrays
You can declare an array and specify its size when you know how many elements you’ll need.
Example 1: Declaring an Integer Array
int numbers[5]; // An array of 5 integersYou can also initialize the array with values at the time of declaration:
int numbers[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // An array initialized with valuesIf you don’t specify the size, the compiler will infer it from the number of elements provided:
int numbers[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // Array size is 5For character arrays (strings), you can declare them like this:
char name[] = "John"; // An array of characters storing a stringAccessing Array Elements
Array elements are accessed using the index, with the first element being at index 0.
Example 2: Accessing and Modifying Elements
int numbers[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
printf("First element: %d\n", numbers[0]); // Output: 10
printf("Third element: %d\n", numbers[2]); // Output: 30
// Modifying an element
numbers[2] = 35;
printf("Modified third element: %d\n", numbers[2]); // Output: 35Iterating Over Arrays
One common operation with arrays is iterating over the elements. This is usually done with loops.
Example 3: Iterating Through an Array Using a for Loop
int numbers[] = {5, 10, 15, 20, 25};
int size = sizeof(numbers) / sizeof(numbers[0]); // Determine array size
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf("Element at index %d: %d\n", i, numbers[i]);
}Multidimensional Arrays
C supports multidimensional arrays, where arrays have more than one dimension (e.g., arrays of arrays). The most common multidimensional array is the 2D array, often used to represent matrices or grids.
Example 4: Declaring a 2D Array
int matrix[2][3] = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6}
};To access an element from a 2D array, you use two indices:
printf("Element at [0][1]: %d\n", matrix[0][1]); // Output: 2Passing Arrays to Functions
In C, arrays can be passed to functions by reference, which means the function works with the original array rather than a copy of it.
Example 5: Passing an Array to a Function
void printArray(int arr[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int numbers[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int size = sizeof(numbers) / sizeof(numbers[0]);
printArray(numbers, size);
return 0;
}Output:
10 20 30 40 50Common Use Cases of Arrays
- Sorting Algorithms: Arrays are frequently used to store data that needs to be sorted (e.g., with the bubble sort or quicksort algorithm).
- Searching: Arrays are used to implement search algorithms like linear and binary search.
- Matrices: Multidimensional arrays are often used to represent mathematical matrices and perform matrix operations.
Conclusion
Arrays are a fundamental concept in C programming, providing a simple and efficient way to store and manipulate multiple values. Whether it’s a one-dimensional array for storing lists of numbers or a multidimensional array for matrices, understanding how arrays work and how to use them is essential for any C programmer. Arrays helpcx you work efficiently with data, making your programs more organized and scalable.
With practice, you’ll be able to use arrays effectively in more complex projects, from algorithm implementations to handling large datasets.


Leave a Reply